|
branch_distribution.h File Reference Detailed Descriptionprobability based branching rule based on an article by J. Pryor and J.W. Chinneck The distribution branching rule selects a variable based on its impact on row activity distributions. More formally, let The impact of a variable on the probability to satisfy a constraint after branching can be estimated by altering the variable contribution to the sums described above. In order to keep the tree size small, variables are preferred which decrease the probability to satisfy a row because it is more likely to create infeasible subproblems. The selection of the branching variable is subject to the parameter
If the parameter The original idea of probability based branching schemes appeared in: J. Pryor and J.W. Chinneck: Definition in file branch_distribution.h. #include "scip/scip.h"Go to the source code of this file.
Function Documentation
creates the distribution branching rule and includes it in SCIP
Definition at line 1298 of file branch_distribution.c. References BRANCHRULE_DESC, BRANCHRULE_MAXBOUNDDIST, BRANCHRULE_MAXDEPTH, BRANCHRULE_NAME, BRANCHRULE_PRIORITY, DEFAULT_ONLYACTIVEROWS, DEFAULT_SCOREPARAM, DEFAULT_USEWEIGHTEDSCORE, EVENTHDLR_NAME, NULL, SCIP_CALL, SCIP_OKAY, SCIPaddBoolParam(), SCIPaddCharParam(), SCIPallocMemory, SCIPincludeBranchruleBasic(), SCIPincludeEventhdlrBasic(), SCIPsetBranchruleCopy(), SCIPsetBranchruleExecLp(), SCIPsetBranchruleExitsol(), SCIPsetBranchruleFree(), SCIPsetEventhdlrFree(), SCOREPARAM_VALUES, and TRUE. Referenced by SCIP_DECL_BRANCHCOPY(), and SCIPincludeDefaultPlugins().
calculate the variable's distribution parameters (mean and variance) for the bounds specified in the arguments. special treatment of infinite bounds necessary
Definition at line 235 of file branch_distribution.c. References NULL, SCIP_VARTYPE_CONTINUOUS, SCIPisInfinity(), SCIPisNegative(), and SQUARED. Referenced by calcBranchScore(), rowCalculateGauss(), and varProcessBoundChanges().
calculates the cumulative distribution P(-infinity <= x <= value) that a normally distributed random variable x takes a value between -infinity and parameter The distribution is given by the respective mean and deviation. This implementation uses the error function erf(). calculates the cumulative distribution P(-infinity <= x <= value) that a normally distributed random variable x takes a value between -infinity and parameter The distribution is given by the respective mean and deviation. This implementation uses the error function SCIPerf().
Definition at line 280 of file branch_distribution.c. References SCIP_Real, SCIPdebugMessage, SCIPerf(), SCIPisFeasLE(), SCIPisFeasZero(), SCIPisNegative(), sqrt(), and SQRTOFTWO. Referenced by SCIProwCalcProbability().
calculates the probability of satisfying an LP-row under the assumption of uniformly distributed variable values. For inequalities, we use the cumulative distribution function of the standard normal distribution PHI(rhs - mu/sqrt(sigma2)) to calculate the probability for a right hand side row with mean activity mu and variance sigma2 to be satisfied. Similarly, 1 - PHI(lhs - mu/sqrt(sigma2)) is the probability to satisfy a left hand side row. For equations (lhs==rhs), we use the centeredness measure p = min(PHI(lhs'), 1-PHI(lhs'))/max(PHI(lhs'), 1 - PHI(lhs')), where lhs' = lhs - mu / sqrt(sigma2).
Definition at line 344 of file branch_distribution.c. References MAX, MIN, NULL, SCIP_Real, SCIPcalcCumulativeDistribution(), SCIPdebug, SCIPdebugMessage, SCIPisFeasEQ(), SCIPisFeasGE(), SCIPisFeasLE(), SCIPisInfinity(), SCIPprintRow(), SCIProwGetLhs(), SCIProwGetName(), and SCIProwGetRhs(). Referenced by calcBranchScore().
update the up- and downscore of a single variable after calculating the impact of branching on a particular row, depending on the chosen score parameter
Definition at line 524 of file branch_distribution.c. References NULL, SCIP_INVALIDCALL, SCIP_OKAY, SCIPerrorMessage, SCIPisFeasGE(), SCIPisFeasLE(), SCIPisGT(), and SCIPisLT(). Referenced by calcBranchScore(). |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||



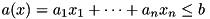 be a row of the LP. Let further
be a row of the LP. Let further 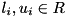 denote the (finite) lower and upper bound, respectively, of the
denote the (finite) lower and upper bound, respectively, of the 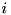 -th variable
-th variable 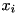 . Viewing every variable
. Viewing every variable 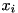 as (continuously) uniformly distributed within its bounds, we can approximately understand the row activity
as (continuously) uniformly distributed within its bounds, we can approximately understand the row activity 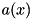 as a gaussian random variate with mean value
as a gaussian random variate with mean value ![$ \mu = E[a(x)] = \sum_i a_i\frac{l_i + u_i}{2}$](form_64.png) and variance
and variance 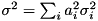 , with
, with 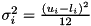 for continuous and
for continuous and 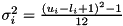 for discrete variables. With these two parameters, we can calculate the probability to satisfy the row in terms of the cumulative distribution of the standard normal distribution:
for discrete variables. With these two parameters, we can calculate the probability to satisfy the row in terms of the cumulative distribution of the standard normal distribution: 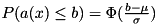 .
.